Horizontal Translations
There are four types of transformations possible for a graph of a function. They are:
- Rotations
- Translations
- Reflections, and
- Dilations
Further, translation can be divided into two different types, i.e.,
- Horizontal translation
- Vertical translation
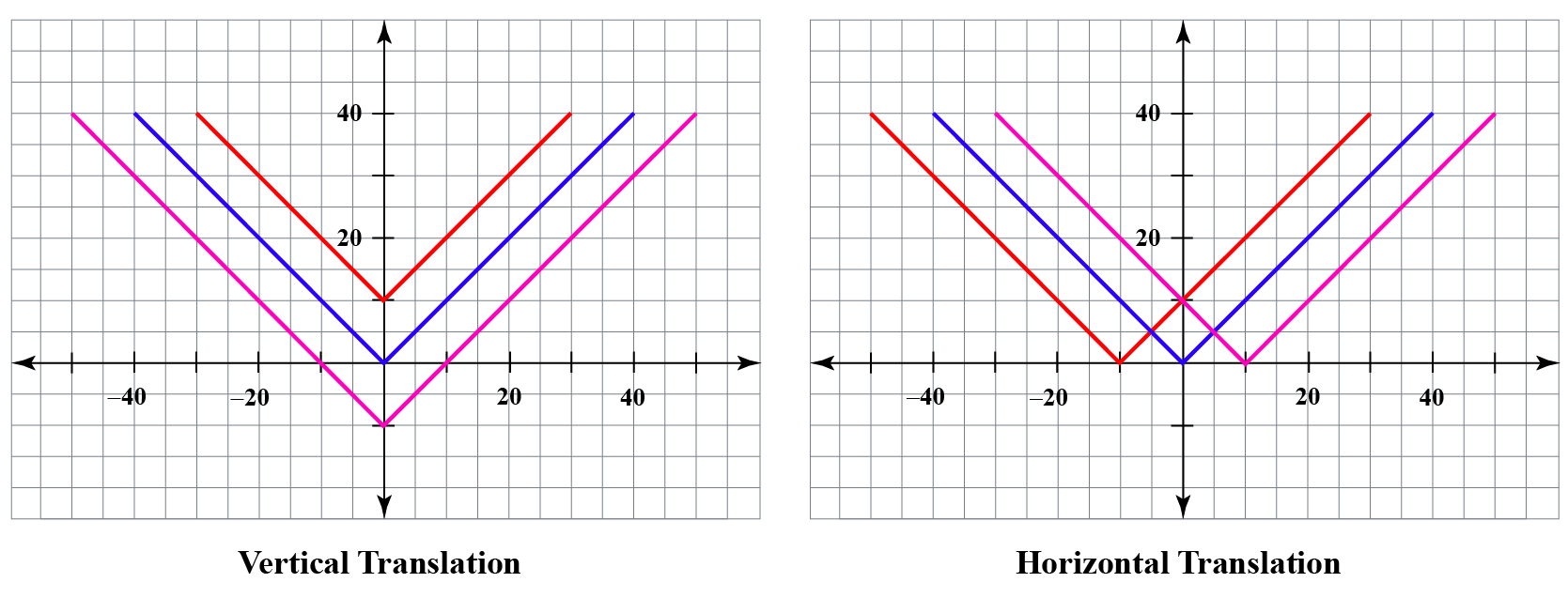
In this section, we will learn about horizontal translation in detail and practice solving questions around it.
Try your hand at solving a few interesting interactive questions at the end of the page.
Lesson Plan
What Is a Horizontal Translation?
Horizontal Translation: Definition
Horizontal translation refers to the movement toward the left or right of the graph of a function by the given units.
The shape of the function remains the same.
It is also known as the movement/shifting of the graph along the x-axis.
For any base function \(f(x)\), the horizontal translation towards positive x-axis by value \(k\) can be given as:
\(g(x) = f(x-k)\)
In horizontal translation, each point on the graph moves \(k\) units horizontally and the graph is said to translate \(k\) units horizontally.
| Horizontal translation for \(f(x) = f(x \pm k)\) |
Horizontal Translation: Examples
The following is the graph of \(f\left( x \right) = \left| x \right|\).

The horizontal translation toward the right side by 1 unit in the above function graph can be given as:
\(g\left( x \right) = f\left(x \right) = \left| x - 1 \right|\)
The graph of the given function after the desired horizontal translation is achieved can be plotted by shifting it toward right by 1 unit.

Similarly, the graph of \(h\left( x \right) = f\left( x + 1\right) = \left| x + 1 \right|\) can be obtained by shifting the graph of \(f\) by 1 unit to the left.
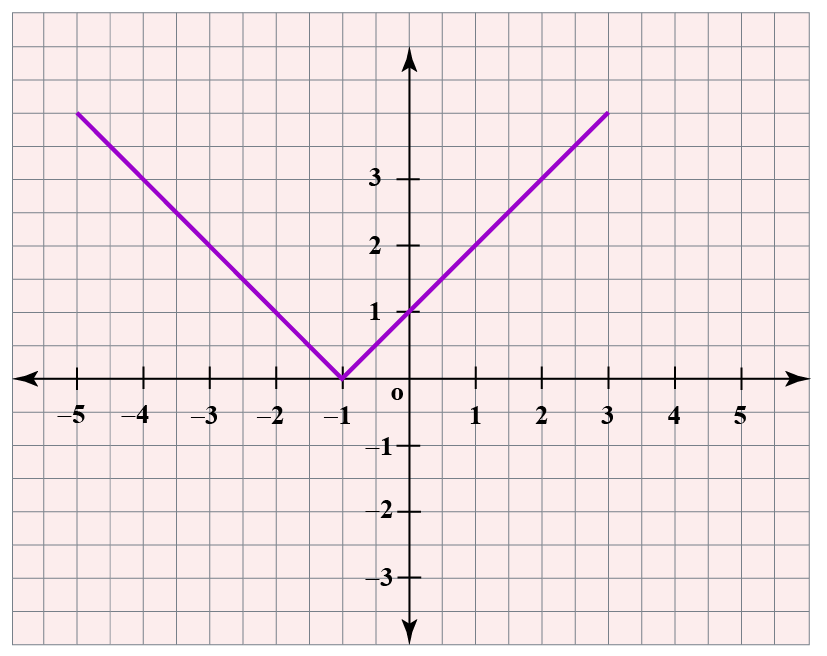
Here, we can observe the horizontal translation of the graph by 1 unit.
The following table shows the coordinates of the point on the different curves after translation:
| The point on \(f(x)\) | The point on \(f(x + k)\) | The point on \(f(x - k)\) |
|---|---|---|
| \( (x, y) \) | \( (x - k, y)\) | \( (x + k, y)\) |
Meanwhile, the shape of the function and domain of the function remains the same.
How Is Horizontal Translation Done?
Let us understand this by an example.
Example
Consider a basic quadratic equation \(f(x) = x^2\).
The graphical representation of this equation is shown below.

Now if we want to translate this graph horizontally, we have to follow the given steps:
Steps
- Select the constant by which we want to translate the function.
Here, we have selected \( \color{orange}{+2}\). - Write the new function as \( g(x) = f(x \pm k)\), where \(k\) is the constant.
Now, our equation of the new function will be:
\[g(x) = f(x \color{orange}{+2}) = (x \color{orange}{+2})^2\]
- Trace the basic function graph again and shift each point in the graph by \(\pm k\), in the horizontal direction (left for +k and right for -k).
Here, we have shifted the graph of \(x^2\) by \(\color{orange}{+2}\) units in the left direction.

- While tracing the graph for a general horizontal translation, we will simply shift the basic function by \(\pm k\) units:

The domain of the function remains the same in both cases.

- Horizontal translation refers to the shifting of the curve along the x-axis by some specific units without changing the shape and domain of the function.
- Horizontal translation of function f(x) is given by g(x) = f(x \(\pm\) k).
Solved Examples
| Example 1 |
Jonas was given a task to plot the curve of the basic function \(f(x) = x^3\) that is translated horizontally by -4 units.
Can you help him with this?
Solution
We know that curve of \(f(x)=x^3\) is:

Since the curve is translated horizontally by -4 units, we can write the equation of the new curve as:
\[g(x) = f(x-4)^3\]
Plotting the curve of \(g(x)\):

\(\therefore\)
|
| Example 2 |
Janice has been asked to plot the curve of \(f(x) = e^{x+2}\).
Can you help her?
Solution
Plotting the curve of \(e^x\):

We know, \(f(x) = e^{x+2}\) is 2 units horizontally translated curve of basic function \(e^x\).
Therefore, shifting the curve of \(e^x\) by 2 units, we get:

| \(\therefore\) The curve of \(f(x) = e^{x+2}\) is plotted. |

- What are the properties of horizontal translation?
- If the function f(x) has coordinates as (x,y), can you find the coordinates of the point on the curve after \(k\) units of horizontal translation?
Interactive Questions
Here are a few activities for you to practice. Select/Type your answer and click the "Check Answer" button to see the result.
Let's Summarize
The mini-lesson targeted the fascinating concept of horizontal translation. The math journey around horizontal translation started with what a student already knew and went on to creatively crafting a fresh concept in the young minds. Done in a way that not only it is relatable and easy to grasp, but also will stay with them forever.
About Cuemath
At Cuemath, our team of math experts is dedicated to making learning fun for our favorite readers, the students!
Through an interactive and engaging learning-teaching-learning approach, the teachers explore all angles of a topic.
Be it worksheets, online classes, doubt sessions, or any other form of relation, it’s the logical thinking and smart learning approach that we, at Cuemath, believe in.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs) on Horizontal Translation
1. What is horizontal translation?
Horizontal translation refers to the movement of the graph of a function to the left or right by a certain number of units.
The shape of the function remains the same.
It is also known as the movement/shifting of the graph along the x-axis.
2. How do you know if a translation is horizontal?
If the base of the original function experiences a shift along the x-axis, the translation spotted is a horizontal translation.
3. What are horizontal shifts?
The movement of the graph of a function along the x-axis is known as a horizontal shift.
4. Why are horizontal translations opposite?
While translating a graph horizontally, it might occur that the procedure is opposite or counter-intuitive. That means:
- For negative horizontal translation, we shift the graph towards the positive x-axis.
- For positive horizontal translation, we shift the graph towards the negative x-axis.
This concept can be understood by analyzing the fact that the horizontal shift in the graph is done to restore the graph's base back to the same origin.
Hence, it is shifted toward the opposite direction of the desired translation.
5. How do you translate a function horizontally?
Horizontal translation refers to the movement of the graph of a function to the left or right by a certain number of units.
The shape of the function remains the same.
It is also known as the movement/shifting of the graph along the x-axis.
6. What is the formula for translation?
The formula for translation or the translation equation is \(g(x) = f(x \pm k) + C\).
7. What is the difference between horizontal and vertical translation?
Vertical translation:
In vertical translation, each point on the graph moves \(k\) units vertically and the graph is said to be translated \(k\) units vertically.
Horizontal translation:
In horizontal translation, each point on the graph moves \(k\) units horizontally and the graph is said to be translated \(k\) units horizontally.
- Live one on one classroom and doubt clearing
- Practice worksheets in and after class for conceptual clarity
- Personalized curriculum to keep up with school