Factoring Methods
In this mini-lesson, we will explore the world of factoring methods in math. You will get to learn about the way to factorize an expression, solving quadratic equations by factoring and other interesting facts around the topic. You can try your hand at solving a few interesting practice questions at the end of the page.
Now, look at the picture given below.
Hey! Don't start thinking which one out of these is your favorite flavor.
Think about the ingredients which are combined together to make such yummy ice-creams.
Similarly, in algebra, we mix a few expressions together to form a new expression.
You can't take out each ingredient from these ice-creams but you can factor all the terms out from the expression.
In this lesson, we will learn various factoring methods and the way to factor quadratic equations.
Lesson Plan
What Is Factoring?
The process of finding the factors is called factoring.
All numbers have factors.
For example, 7 and 3 are the factors of 21.
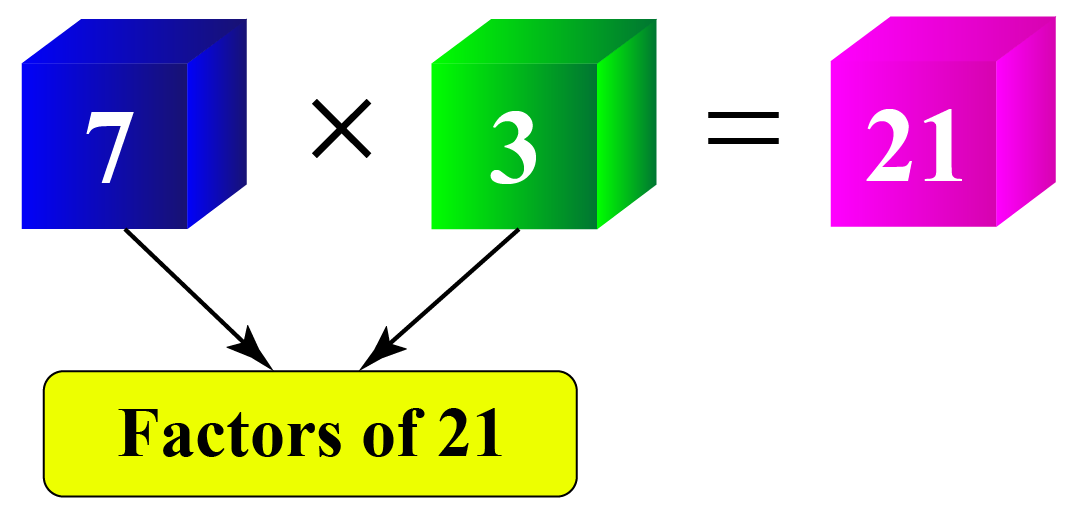
Algebraic expressions also have factors.
For example, \(x\) and \(x-2\) are the factors of \(x^2-2x\)
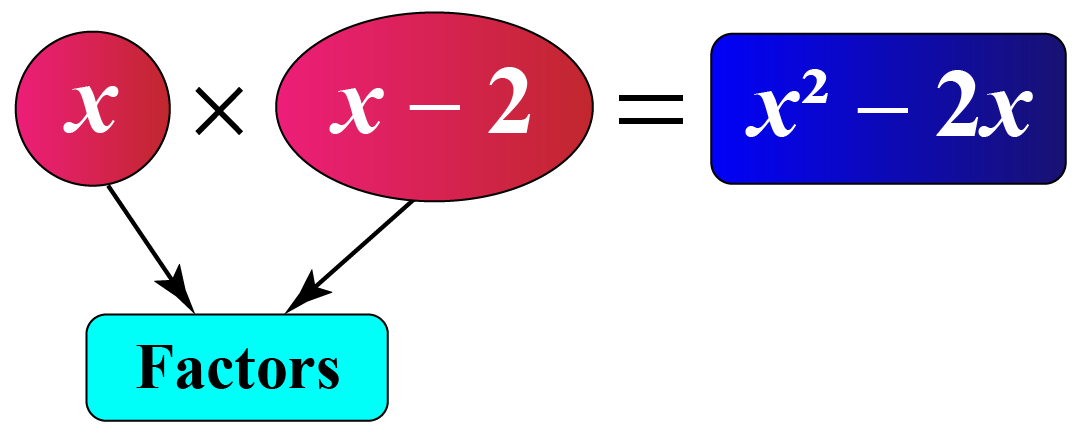
Here, \(x\times 2x\) is the factored form of \(x^2-2x\).
So, factors can be numbers, algebraic expressions, or algebraic variables.
Experiment with the following simulation to see the factors of a few expressions.
Methods of Factoring
We will discuss some systematic methods of factoring algebraic expressions.
Method of Common Factors
Consider a simple example: \(3x+9\)
By factorizing each term we get, \((3\times x)+(3 \times 3)\)
By distributive law, \(3x+9=(3\times x)+(3 \times 3)=3(x+3)\).
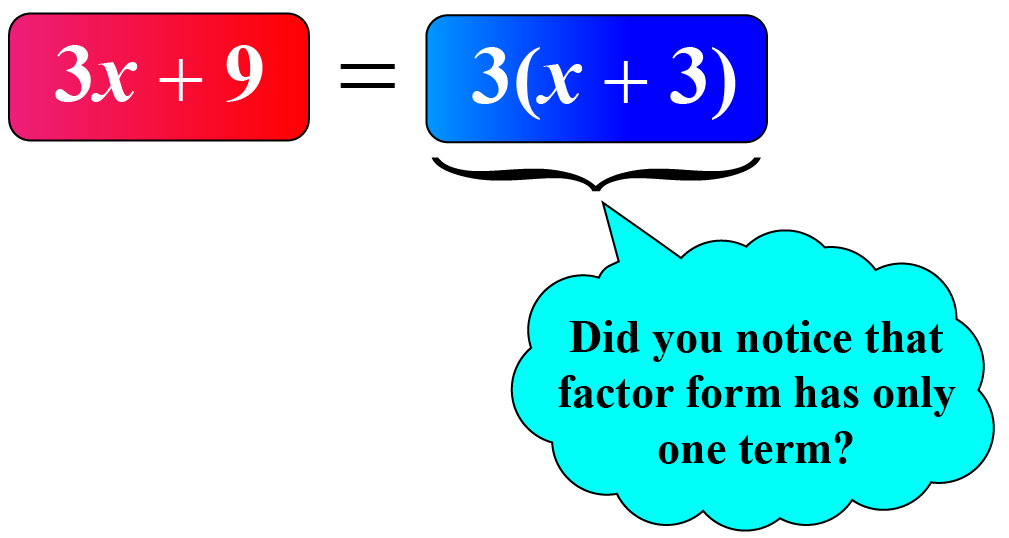
Method of Regrouping
Regrouping allows us to rearrange the terms of the expression that leads to factorization.
Consider an expression: \(2ab+2b+7a+7\)
Notice that there is no single factor common to all the terms.
Let us write \(2ab+2b\) and \(7a+7\) in the factor form separately.
\[\begin{align}2ab+2b&=2b(a+1)\\7a+7&=7(a+1)\end{align}\]
So, \(2ab+2b+7a+7=2b(a+1)+7(a+1)\).
Now, we have a common factor \((a+1)\) on the right-hand side.
The given expression is factorized as \(2ab+2b+7a+7=2b(a+1)+7(a+1)=(2b+7)(a+1)\).
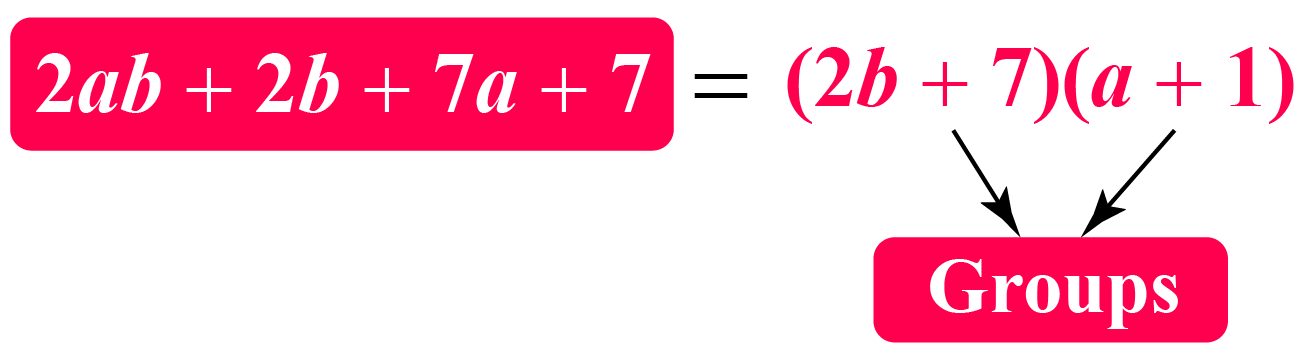
Method Using Algebraic Identities
Remember a few identities that are used for factorization.
| \((a+b)^2=a^2+b^2+2ab\) |
| \((a-b)^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\) |
| \((a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2\) |
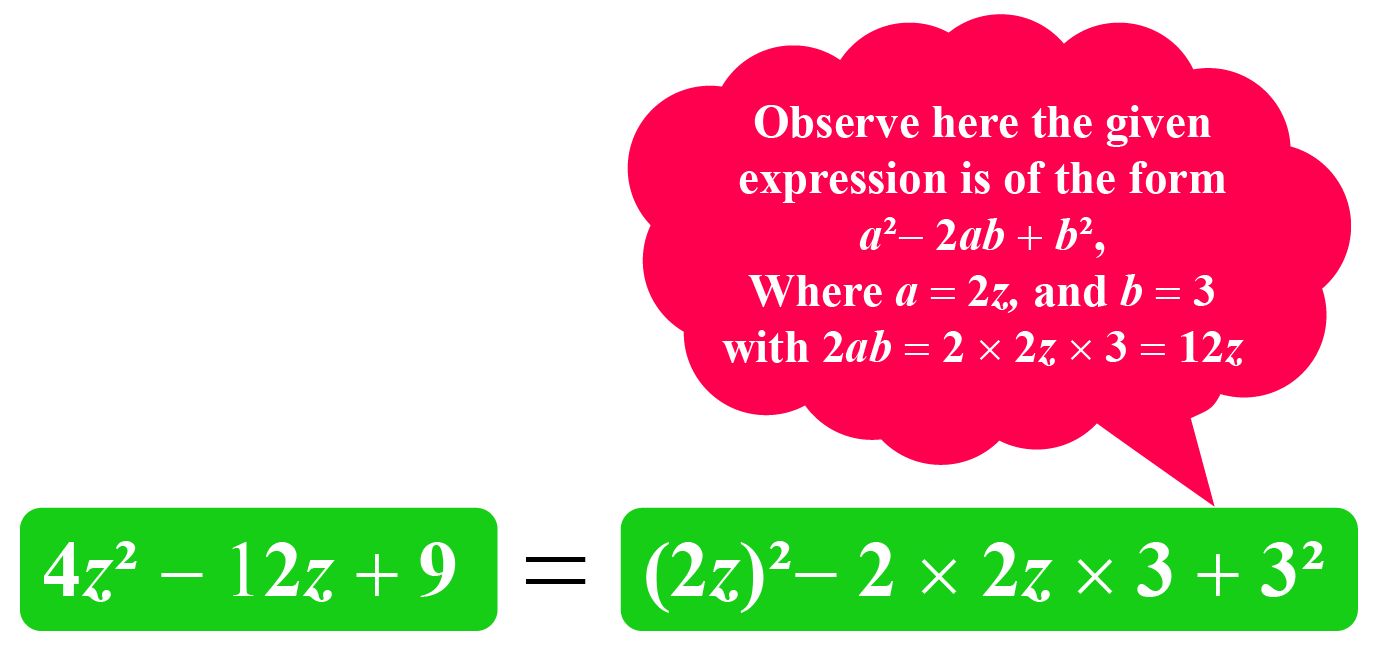
Let's factorize \(4z^{2}-12z+9\)
Observe that \(4z^{2}=(2z)^{2}\), \(12z=2\times 3\times 2z\), and \(9=3^{2}\)
So, we can write \(4z^{2}-12z+9=(2z)^{2}-2\times 2z\times 3+3^{2}=(2z-3)^2\)
How to Factor Trinomials?
Solving Quadratic Equations By Factoring
We’ll do a few examples on solving quadratic equations by factorization.
Example 1: \[4x-12x^2=0\]
Given any quadratic equation, first check for the common factors.
In this example, check for the common factors among \(4x\) and \(12x^2\)
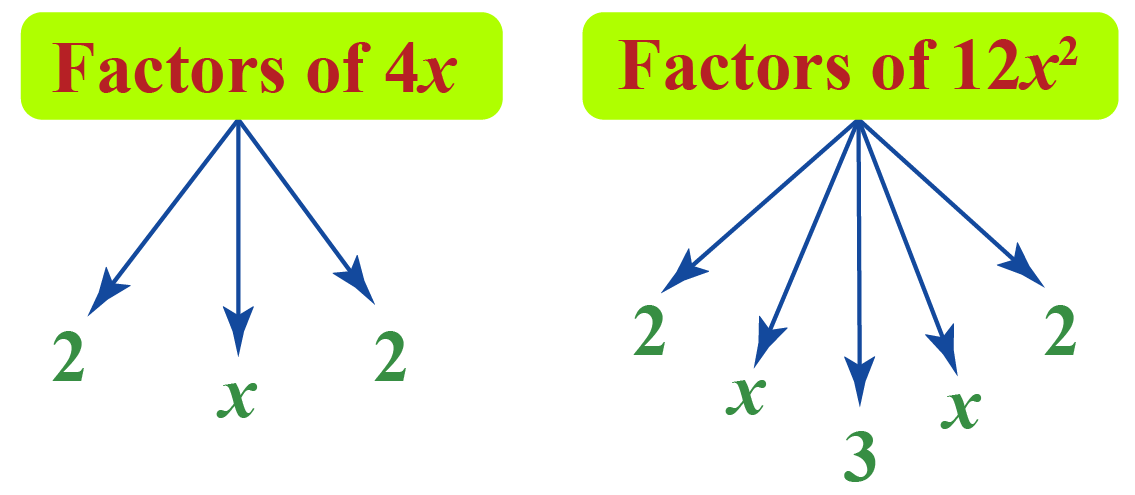
We can observe that \(4x\) is a common factor. Let’s take that common factor from the quadratic equation.
\[\begin{align}4x-12x^2&=0\\4x(1-3x)&=0\end{align}\]
Thus, by factoring the quadratic equation, we get \(4x(1-3x)=0\).
In other words, the quadratic equation can be factored as \((4x)(1-3x)=0\).
Example 2: \[x^2+5x+6=0\]
We’ll factor this in two binomials, namely \((x+a)\) and \((x+b)\).
Expand \((x+a)(x+b)=0\).
\[\begin{align}(x+a)(x+b)&=0\\x(x+b)+a(x+b)&=0\\x^2+bx+ax+ab&=0\\x^2+(a+b)x+ab&=0\end{align}\]
Let’s try to find \(a\) and \(b\) such that \((a+b)\) is mapped to 5 and \(ab\) is mapped to 6.
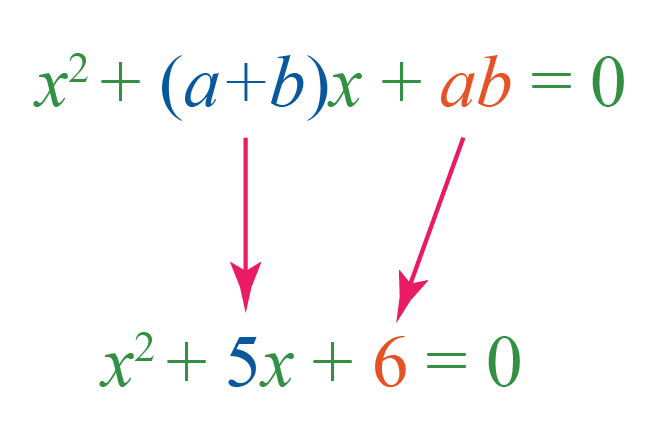
The factors of \(6\) are \(1\), \(2\), \(3\) and \(6\). Find the pairs \(a\) and \(b\) from \(1\), \(2\), \(3\) and \(6\) such that \(a+b=5\) and \(ab=6\)
This is the right pair: \(2\) and \(3\), because, \(2+3 = 5\) and \(2 \times 3=6\)
Thus, the quadratic equation can be factored as \((x+2)(x+3)=0\).
Calculator For Factoring
Here is a calculator for factoring different expressions.

-
The process of finding the factors is called factoring.
-
Factoring helps us to find the solution of any algebraic expression.
-
Factoring allows us to express an expression in a simpler form.
Solved Examples
| Example 1 |
George has a huge rectangular farm.
He knows that the area of the farm is \(528\;\text{ft}^{2}\)

He says "The length of the farm is one more than twice its breadth."
Can you use this information to write the factored form of 528?
Solution
Let the breadth of the farm be \(x\) feet.
So, the length of the farm would be \(2x+1\) feet.
The area of a rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
According to the question,
\[\begin{align}\text{Area of Farm}&=\text{Breadth} \times \text{Length}\\528&=x\times (2x+1)\end{align}\]
| So, the factored form of 528 is \(x(2x+1)\) |
| Example 2 |
Jenny asked Jolly to factorize \(6xy-4y+6-9x\)
Jolly wants to factorize it using the method of regrouping.

Can you help them?
Solution
We observe that we have no common factor among all the terms in the expression \(6xy-4y+6-9x\)
Let's deal with \(6xy-4y\) and \(6-9x\) separately.
\[\begin{align}6xy-4y&=2y(3x-2)\\6-9x&=-3(3x-2)\end{align}\]
So, the given expression can be written as
\[\begin{align}6xy-4y+6-9x&=2y(3x-2)-3(3x-2)\\&=(2y-3)(3x-2)\end{align}\]
| So, factors of \(6xy-4y+6-9x\) are \((2y-3)\) and \((3x-2)\) |
| Example 3 |
Mia is a fitness enthusiast who runs every morning.
The park where she jogs is rectangular in shape and measures 12 feet by 8 feet.
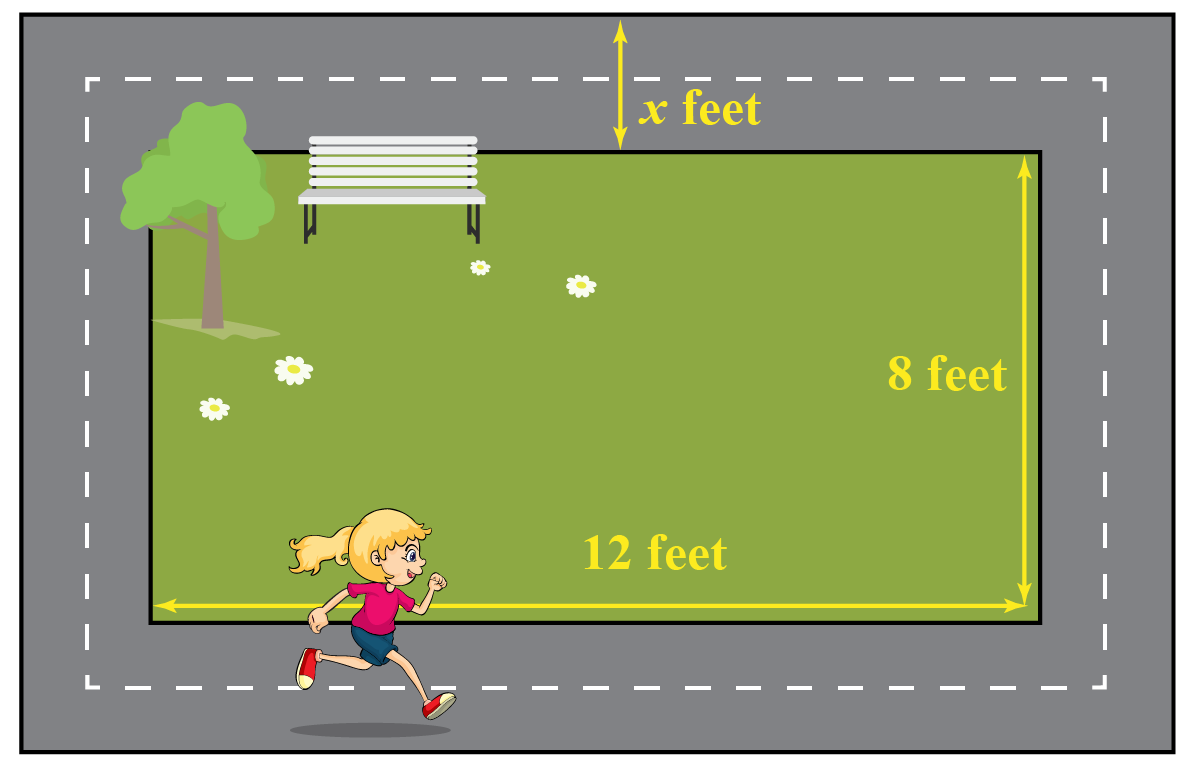
An environmentalist group plans to revamp the park and decides to build a pathway surrounding the park.
This would increase the total area to 140 sq. ft.
What will be the width of the pathway?
Solution
Let’s denote the width of the pathway as \(x\).
Then, the length and breadth of the outer rectangle is \((12+2x)\;\text{ft.}\) and \((8+2x)\;\text{ft.}\)
According to the question,
\[\begin{align}(12+2x)(8+2x)&=140\\2(6+x)\cdot 2(4+x)&=140\\(x+6)(x+4)&=35\\x^2+10x-11&=0\end{align}\]
So, we have to find the solution of the quadratic equation \(x^2+10x-11=0\)
\[\begin{align}x^2+11x-x-11&=0\\x(x+11)-(x+11)&=0\\(x+11)(x-1)&=0\\x&=1,-11\end{align}\]
Since the length can’t be negative, we take \(x=1\)
| So, the width of the pathway will be 1 feet. |
Sometimes working with a hard expression is difficult. But don’t worry!
Here are a few tips and tricks for you to follow while factoring.

- Check out for any common terms in an expression and take the greatest common factor.
- Check if any algebraic identities are applicable in the expression.
- Keep factoring the expression until you reach the simplest form, that is, the form that is not further divisible.
Interactive Questions
Here are a few activities for you to practice.
Select/type your answer and click the "Check Answer" button to see the result.
Let's Summarize
The mini-lesson targeted the fascinating concept of factoring methods. The math journey around factoring methods starts with what a student already knows, and goes on to creatively crafting a fresh concept in the young minds. Done in a way that not only it is relatable and easy to grasp, but also will stay with them forever. Here lies the magic with Cuemath.
About Cuemath
At Cuemath, our team of math experts is dedicated to making learning fun for our favorite readers, the students!
Through an interactive and engaging learning-teaching-learning approach, the teachers explore all angles of a topic.
Be it worksheets, online classes, doubt sessions, or any other form of relation, it’s the logical thinking and smart learning approach that we, at Cuemath, believe in.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How to factor trinomials with a leading coefficient?
The following steps show how to factor trinomials with a leading coefficient.
- Write the trinomial in the standard form.
- Take the greatest common factor out if it exists.
- Find the product of the leading coefficient and the constant term.
- Determine the factors of the product found in step 3 and check which factor pair will result in the coefficient of \(x\).
- After choosing the appropriate factor pair, keep the sign in each number such that while operating them we get the result as the coefficient of \(x\) and on finding their product the number is equal to the number found in step 3.
- Now, you have 4 terms in the expression and so we use the method of regrouping to factorize.
2. How to factor perfect square trinomials?
Use the algebraic identities mentioned below to factor perfect square trinomials.
- \((a+b)^2=a^2+b^2+2ab\)
- \((a-b)^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\)
