Denominator
Denominator is the number that is placed below the horizontal line of a fraction. It is the bottom number of a fraction that shows the total number of equal parts an object is divided into. Let us learn more about the denominator in this page.
| 1. | What is a Denominator? |
| 2. | Numerator and Denominator |
| 3. | Examples of Denominator |
| 4. | Common Denominator |
| 5. | FAQs on Denominator |
What is a Denominator?
A denominator is the part of a fraction that comes below the fractional bar. The denominator shows the total amount of parts that make up a whole. A fraction can be identified by a horizontal bar between two numbers and sometimes the symbol "/". This bar or symbol is known as the "fractional bar." The number on the top is known as the "numerator", and the number below the fractional bar is known as the "denominator".
For any fraction a/b, 'a' is the numerator and 'b' is the denominator. Fractions represent a part of a whole. Mathematically, it is shown by the division of two numbers. For example, 1/4 is one part out of the four equal parts created from that one whole thing. Here, 1 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator.

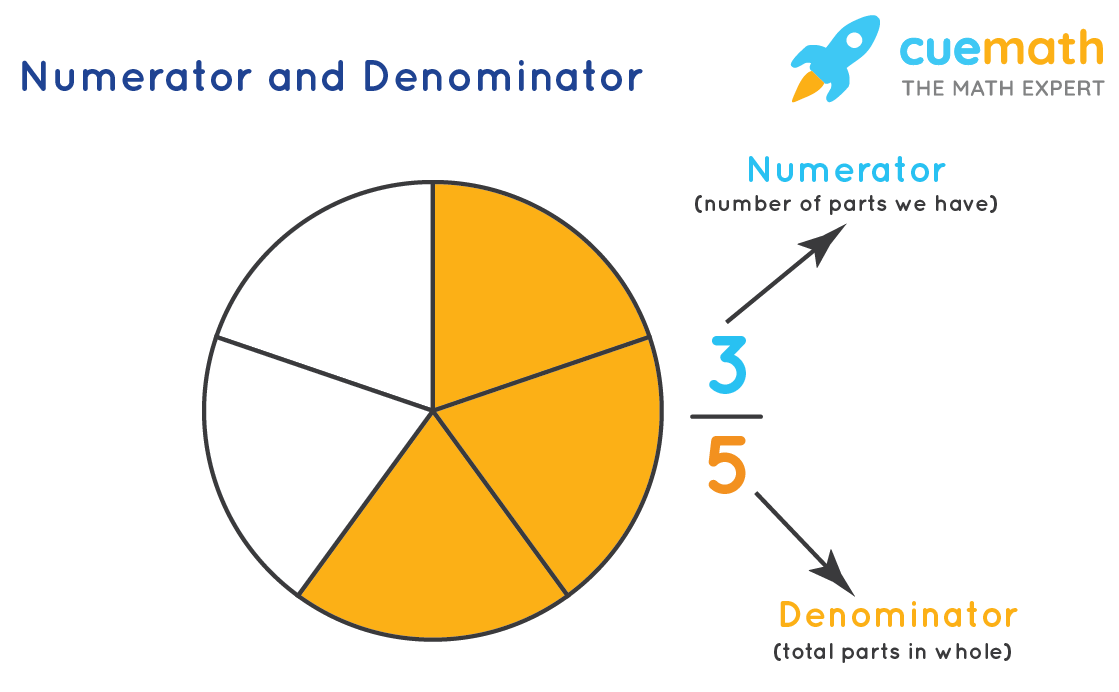
Numerator and Denominator
The denominator indicates how many parts make up a unit or a whole. The numerator indicates the number of parts that we have selected out of the total number of equal parts. For example, in the fraction 3/5, the numerator 3 represents 3 equal parts selected by us, and the denominator 5 represents the 5 equal parts created initially. The 5 equal parts make up a whole. Observe the fraction model given below. The shaded portion represents the fraction 3/5. Three portions are shaded (Numerator) out of the total 5 portions created (denominator).
Examples of Denominator
The examples of denominators can be understood in a simple way. In the fraction x/y, x is the numerator and y is the denominator. Apart from numbers, variables are also expressed in the same form such as x/y, a/b, p/q, where y, b and q are the denominators respectively. Some examples of denominators are given in the table below:
Fractions |
Denominator |
|---|---|
|
1/3 |
3 |
|
11/20 |
20 |
|
6/(x-2y) |
x-2y |
|
3x/8y |
8y |
|
(i × j) /5 |
5 |
|
(p+3)/(q+9) |
q+9 |
Common Denominator
When the denominators of two or more fractions are the same, they are known as the common denominators. The least common denominator (LCD) is the smallest number that can be a common denominator for a given set of fractions. Addition and subtraction of fractions and comparing two or more fractions is possible only if the fractions have common denominators. For example, if we need to add 3/8 + 1/8. Since the denominators are the same, they are like fractions and can be instantly added up and the result will be 3/8 + 1/8 = 4/8 = 1/2.
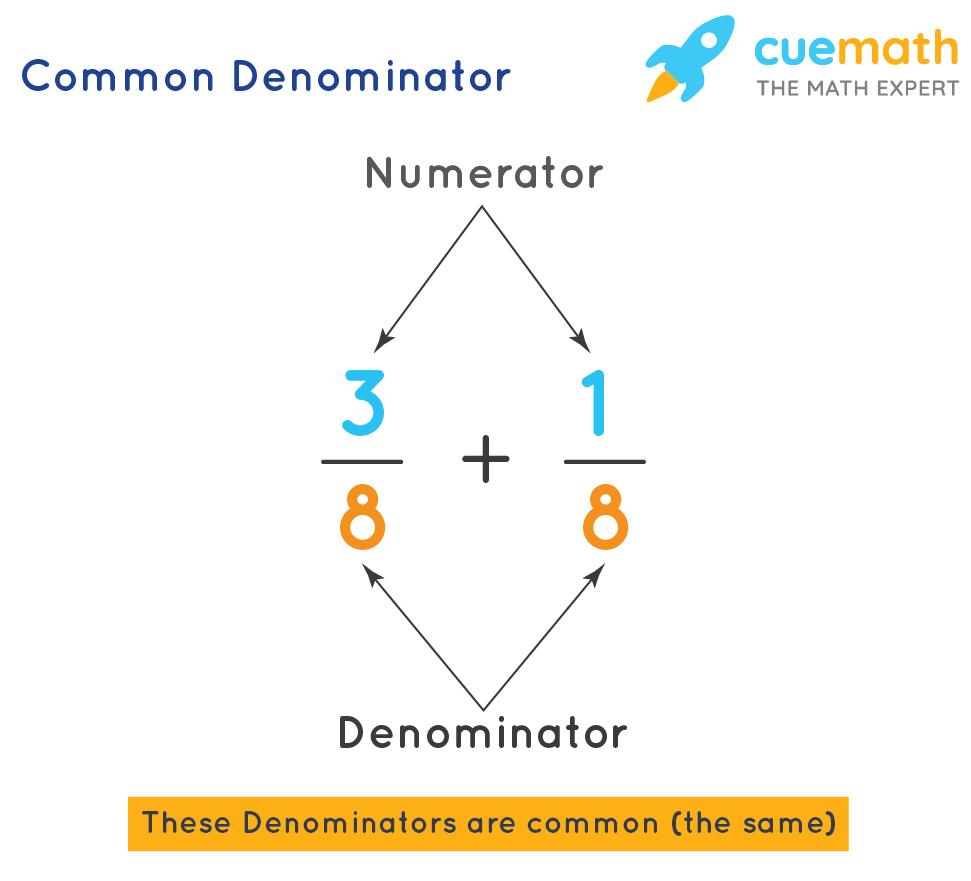
Like fractions are the fractions that have the same denominators. Example: 5/15, 3/15, 17/15, and 31/15. Unlike fractions are the fractions which have different denominators. Example: 2/7, 9/11, 3/13, and 39/46. Let us see some examples here to add and subtract fractions with common denominators.
- 2/2 + 3/2 = (2+3)/2 = 5/2
- 6/7 - 2/7 = (6-2)/7 = 4/7
For different denominators, we need to convert the given unlike fractions to like fractions by changing the fractions to equivalent fractions having the same denominator. This can be done by finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of the denominators, which is known as LCD (Least Common Denominator). Let us understand this with the help of an example,
Example: Add 1/2 + 1/3
Solution:
- Step 1: Since the given fractions are unlike fractions, we will find the LCM of the denominators 2 and 3. The LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
- Step 2: Now, we will multiply the first fraction 1/2 with 3/3, this will result in an equivalent fraction 3/6. Similarly, we will multiply the second fraction 1/3 with 2/2, this will result in 2/6.
- Step 3: This step will convert both the fractions to like fractions, that is, 3/6 and 2/6.
- Step 4: Now, that the denominators are the same, we can add the numerators while the denominator will remain the same, that is, 3/6 + 2/6 = 5/6. Therefore, the sum of 1/2 + 1/3 = 5/6.
Important Notes
- A denominator must be an integer.
- A denominator can never be zero because zero parts can never make up a whole.
- The term denominator is widely used in the concepts of rational numbers, ratios and proportions, and division concepts.
☛ Related Articles
Denominator Examples
-
Example 1: Riya ordered a pizza at a restaurant. Each piece of pizza represents a part of a whole. The pizza is divided into 6 equal slices. If she ate one slice, then write this fact in the form of a fraction and write the denominator of the fraction.
Solution:
Total number of slices of pizza = 6
Total number of pieces eaten by Riya = 1
The fraction of pizza that she ate = 1/6
Here, 6 is the number that denotes the total number of slices of pizza. Therefore, the denominator is 6.
-
Example 2: A grandmother bought an apple for her grandchild. She cut it into 4 pieces. If she gives one piece of an apple to the child, express this fact in the form of a fraction and also write the denominator of the fraction.
Solution:
The total number of pieces of the whole apple = 4. If 1 piece of an apple is given to the child, the fraction for this fact will be expressed as 1/4.
So, the denominator is 4, which denotes the total number of pieces of the apple.
-
Example 3: If the denominators of the following fractions are the same, 4/6, 2/6, 3/6, what kind of fractions will they be called?
Solution:
Since all the given fractions have the same denominator, these will be called like fractions.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Denominator in Math?
The number that is written below the fractional bar in a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator shows the total number of parts that make up a whole.
What is an Example of a Denominator?
A denominator can be easily identified in a fraction. In the fraction 4/7, the number (4) that is written on top of the fractional bar is the numerator, whereas, the number (7) which is written below the fractional bar is known as the denominator. Therefore, in the given fraction 4/7, the denominator is 7.
Where is the Denominator in a Fraction Located, Top or Bottom?
The denominator is located on the bottom of the fractional bar of a fraction. For example, in the fraction 3/4, 4 is the denominator.
Can a Denominator be 0?
No, a denominator can never be zero because a fraction becomes undefined if the denominator has the value 0. No object can be divided into 0 equal parts.
Can a Denominator be Negative?
Yes, a denominator can have a negative sign. Although only one common sign is placed in a fraction just before the fractional bar. In other words, the fraction as a whole represents only one sign, which is decided on the basis of the sign of the numerator and the denominator. For example, if both the numbers in the numerator and the denominator have a negative sign or a positive sign, then the overall fraction will show a positive sign. This means, (-3)/(-2) = 3/2. However, when they have different signs, then the fraction will show a negative sign, that is (-4)/(+3) = -4/3. Individually, the numerator and the denominator can have different signs if they have variables or any other symbols.
What is the Denominator in the Fraction 2/5?
In the given fraction 2/5, 2 is the numerator and 5 is the denominator.
What is the Difference Between a Numerator and a Denominator?
The numerator of a fraction represents the number of equal parts that we use or select from the whole, whereas, the denominator represents the total number of equal parts given. If we divide a cake into 5 equal parts and eat 2, then 5 becomes the denominator and 2 becomes the numerator. This is represented as 2/5. The numerator of a fraction is placed on top of the fractional bar and the denominator is always placed below the fractional bar.
What is a Least Common Denominator?
Whenever two or more fractions have the same denominators, they are called common denominators. The Least Common Denominator (LCD) refers to the smallest number that is a common denominator for a given set of fractions. For example, let us find the least common denominator of the following fractions: 2/3, 4/6, and 3/12. The denominators of the given fractions are 3, 6, and 12. Let us find out their LCD by the listing multiples method:
- The multiples of 3 can be listed as 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, ...
- The multiples of 6 can be listed as 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, ...
- The multiples of 12 can be listed as 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, ...
Thus, we can conclude that the least common multiple of 3, 6, and 12 is 12. Therefore, the least common denominator for the given fractions, 2/3, 4/6, and 3/12 is 12.
How to Rationalize the Denominator?
When we rationalize the denominator, we move a root from the denominator to the numerator. In other words, we bring the fraction to its simplest form making the denominator rational. Numbers like 2, 3, and 4 are rational and numbers like √3 and √4 are irrational. For example, to rationalize the denominator in the given term 1/√5, we will multiply the numerator and the denominator by a root. Here, we will multiply 1/√5 by √5/√5. This will result in √5/5. This process is known as rationalizing the denominator.
visual curriculum